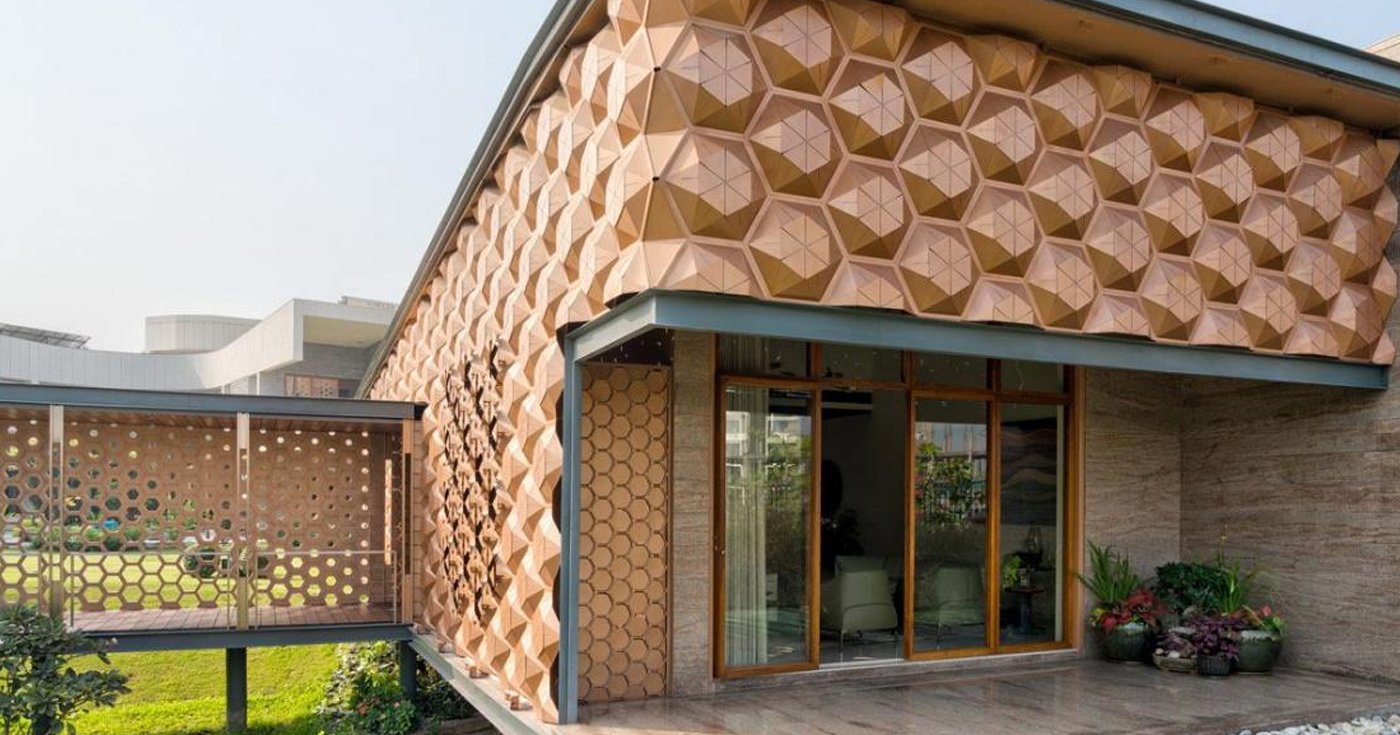
Introduction
The expression “regenerative” defines the practice of restoring, renewing, or revitalising their sources of energy and materials. A regenerative design utilises the idea of the entire system to generate flexible and equitable systems that would understand the needs of society with absolute integrity towards nature. Regenerative architecture is the way of involving the natural world as the method for and creator of architecture. It reacts to the living and natural systems in a location that becomes the “building units” of the architecture.
It is a new way of developing structures that goes beyond just sustainability. It is different from sustainably designed buildings, which are based on the concept of only using the minimum resources you need. Regenerative buildings are designed and operated to reverse the damage and have a net-positive impact on the environment. As architects, designers, and planners, we have the unique opportunity to provide this mind shift.
History
The regenerative architecture was initially a way of reconstruction post-war in several areas of Europe’s devastated cities, which were then affected by the post-industrial era in the mid-1970s, which benefited regenerative projects. Regenerative Architecture first came to notice in 1976. When Wiley published Lyle’s book on “Regenerative Design for Sustainable Development”. John T. Lyle believed in innovative designs which broke the traditional norms of architecture, in a way that resources can be renewed without depleting natural resources.
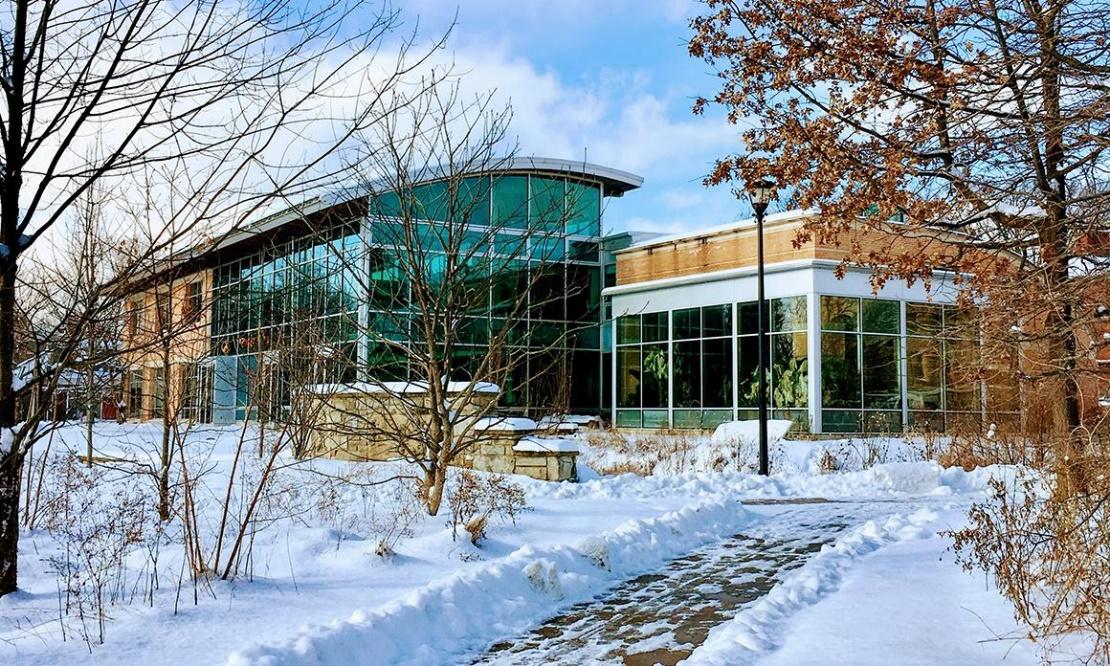

Adam Joseph Lewis Center for Environmental Studies is one of the earliest examples of Regenerative Architecture. William McDonough had a sincere dialogue with the client to understand exactly how they expected the building to develop in terms of regenerative design. Adam Joseph Lewis Center for Environmental Studies has green roofs and skins, storing rainwater, wastewater treatment, thermal efficient construction, and energy consumption & production.
Difference between Sustainable and Regenerative architecture
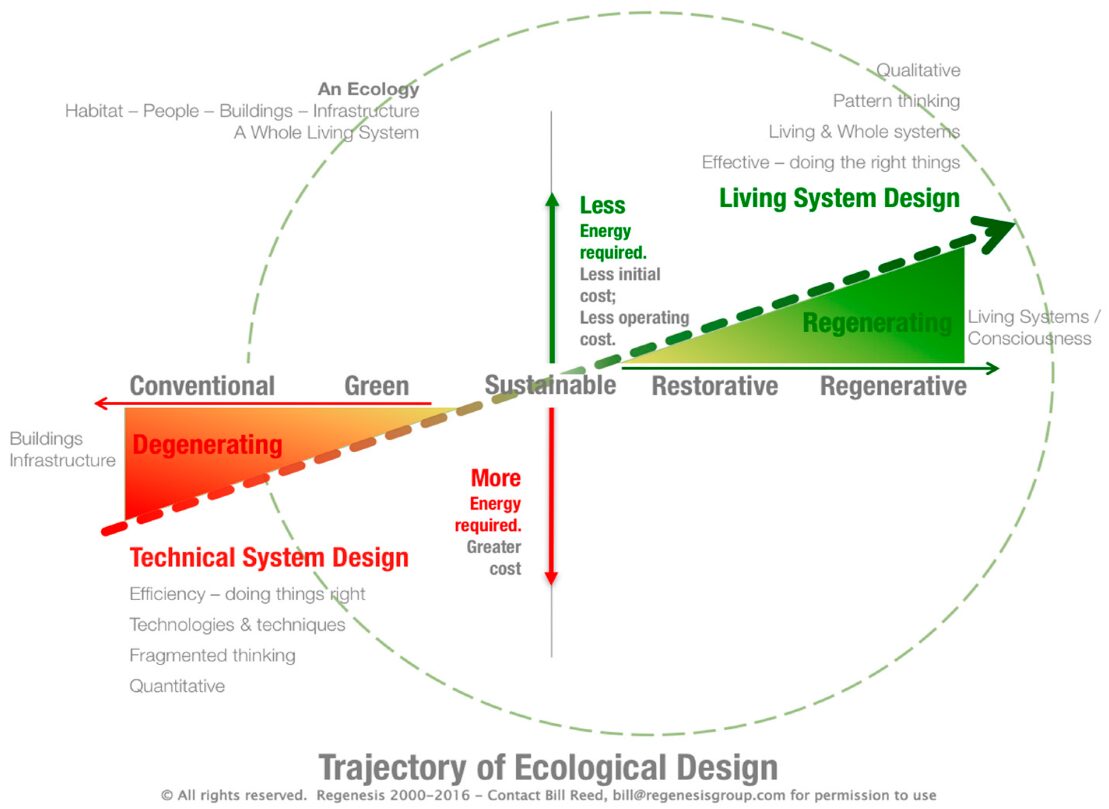
The meaning of the sustainable design, as depicted in the above diagram, is based on the concept that it does not harm nature and without more than the required amount. Sustainable design is now considered an obsolete concept based on the notion that there is merely any need to sustain our existence, conveniences, routines, and environments. As humankind continues to use resources, it is guaranteed that those resources will ultimately be depleted or extinct.
Sustainable design is a way to reduce the negative impact on the environment by improvising the building efficiency, but the severity of damage caused to the environment in recent years has been catastrophic. Because of this reason, there is a need to think about designing in a way that it sustains not only for years, but restores itself to cause no loss.
The regenerative design, however, is a means of living that allowed us to use the resources we need and replenish those resources Regenerative practices identify how natural systems like our environment have been affected because of various forms of pollution, and the techniques applied helped to restore systems to improved productivity.
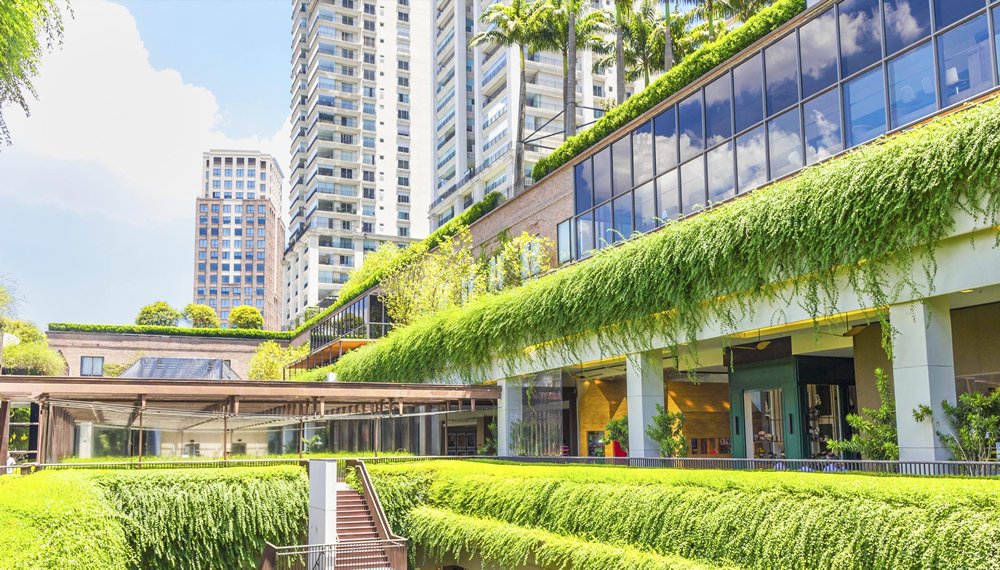

Regenerative and sustainable actions overlap and essentially incorporate nearly the same practices. The regenerative design states more importance of conservation and biodiversity rather than preservation. Regenerative design helps realise humans are a part of the natural ecosystems. Hence, to exclude people is to create densely populated areas that destroy or exceed the limits of the pockets of existing ecosystems. Regenerative architecture is the way of preserving pockets of ecosystems without letting them deplete and replenish naturally.
Therefore, sustainably designed buildings are based on the concept of only using the minimum resources you need. Regenerative buildings are designed and operated to reverse the damage and have a net-positive impact on the environment.
Features of Regenerative Design
- Generating And Storing Energy (Net-Zero Energy)

